What Is Due Diligence?
Due diligence (DD) refers to the comprehensive assessment of a company’s financial, economic, legal and fiscal aspects before carrying out a potential business or financial transaction.
It encompasses more than just gathering additional information and data of an entity to make an informed business decision. DD is a widely adopted practice by various business associations during funding rounds or when undergoing mergers and acquisitions (M&As).
Why Is Due Diligence Important?
In recent times, investors have become extremely cautious to conduct due diligence, owing to the volatility experienced in the startup ecosystem. Examples of startups like BharatPe, which faced several allegations of irregularities, and the collapse of GoMechanic and Zilingo have made investors more watchful.
However, it is worth noting that DD is not mandatory legally. Rather, it entails a series of standard procedures that entities are advised to undertake prior to entering into business agreements.
What Are The Different Types Of Due Diligence?
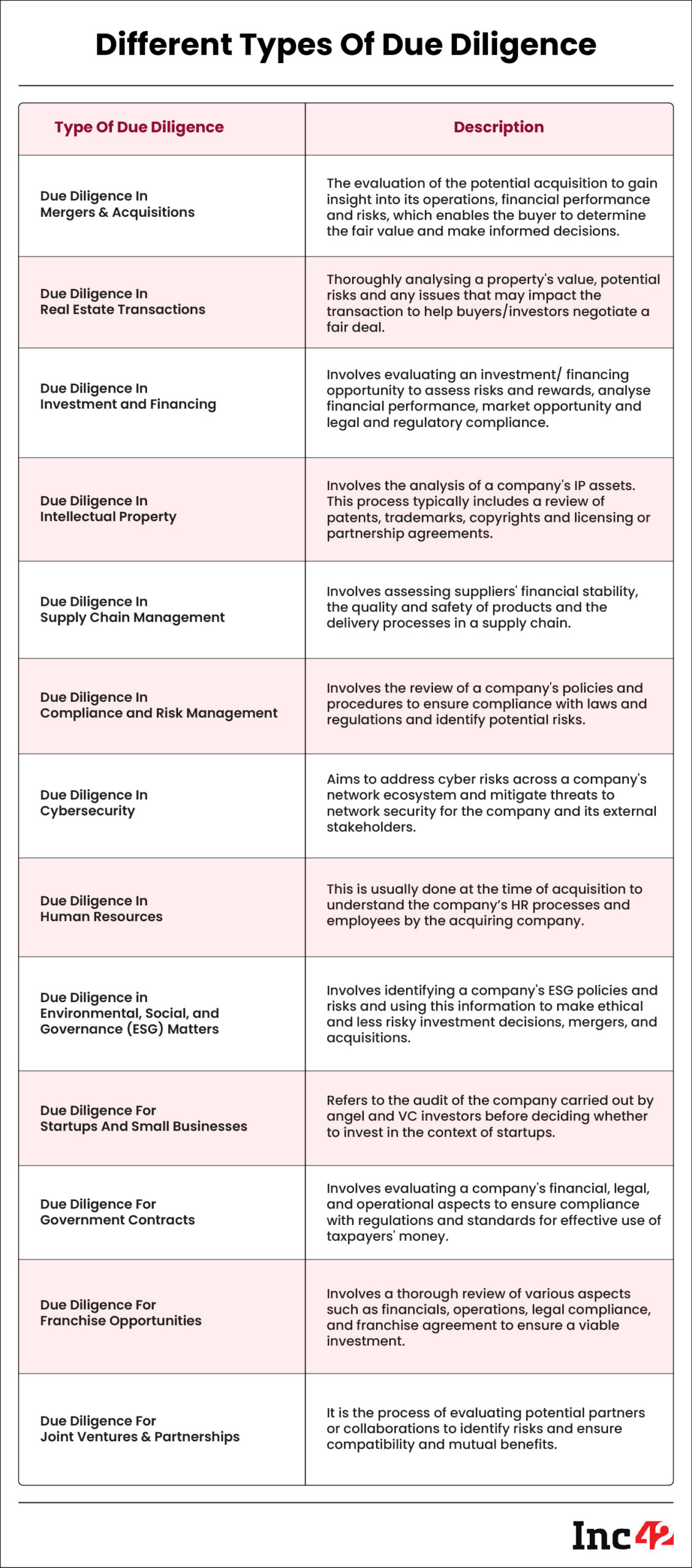
Due diligence is performed in various sectors and for various purposes, including:
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)
- Real estate
- Investment & financing
- Intellectual property
- Supply chain management
- Compliance & risk management
- Cybersecurity
- Human resources
- Environmental, social and governance (ESG) matters
- Startups and small businesses
- Government contracts
- Franchise opportunities
- Joint ventures and partnerships
What Is The Due Diligence Process Like?
There are a few factors that investors consider:
- The Core Business: Investors typically look into a startup’s core business strategy, the industry it operates in, its competitors and market trends before investors. They also evaluate a team’s expertise and skill sets as well as the founder’s vision before making a decision.
- The Risk: The risk factor is inevitable in startups, especially in the early stages. Investors try to understand the degree of risk associated with a startup to form an opinion of the startup, determine the efforts required to mitigate risks and what steps have already been taken.
- Product/Service Differentiation: A startup’s product USP is what differentiates it from the competition and gives it an advantage over them. Hence, due diligence takes into account the scope of a business by assessing its offerings, talking to the target customers and evaluating its marketing strategy.
- Intellectual Property: It evaluates a startup’s ownership of IP, trademarks, copyrights, and patents, among other things.
Other factors evaluated by an investor may include, legal compliances, financials and IPO and payoffs.
Who Typically Performs Due Diligence?
The Big 4 accounting firms (Deloitte, PwC, EY, and KPMG) are known to conduct DD on behalf of investors, private equity firms and venture capitalists.
What Are The Risks Of Not Conducting Due Diligence?
Failure to conduct due diligence can lead to significant risks, including financial losses, legal issues, reputation damage, and missed opportunities.
How Long Does Due Diligence Usually Take?
It typically takes anywhere between four and six weeks but may extend if investors have specific requests.
What Are Some Common Mistakes Made During Due Diligence?
Focussing too much on a single component can hamper due diligence. For example, investors may focus too much on financials, neglecting other important factors such as cultural fit, long-term growth and sustainability of a business or external factors such as market volatility.
What Is Included In A Due Diligence Report?
A due diligence report includes a thorough analysis of a company’s financials, legal, and operational health, as well as any potential risks and opportunities associated with the investment or acquisition.
How Can Technology Assist In The Due Diligence Process?
Technology can assist in a number of ways, including:
- Automated Data Collection: Technology can automate the collection of data from various sources such as financial reports, regulatory filings and social media, making the process faster and more efficient.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics can help investors identify trends, patterns and anomalies in large datasets, allowing for informed decision-making.
- Artificial intelligence: AI can help automate the analysis of legal documents, such as contracts and patents, and identify potential risks and opportunities.
How Does Due Diligence Differ In M&As And Investments?
Due diligence in M&A involves a comprehensive investigation of a company’s financial, legal and operational records by the buyer. However, the focus is on evaluating potential risks and returns of a company based on its business model, market fit and management team.








